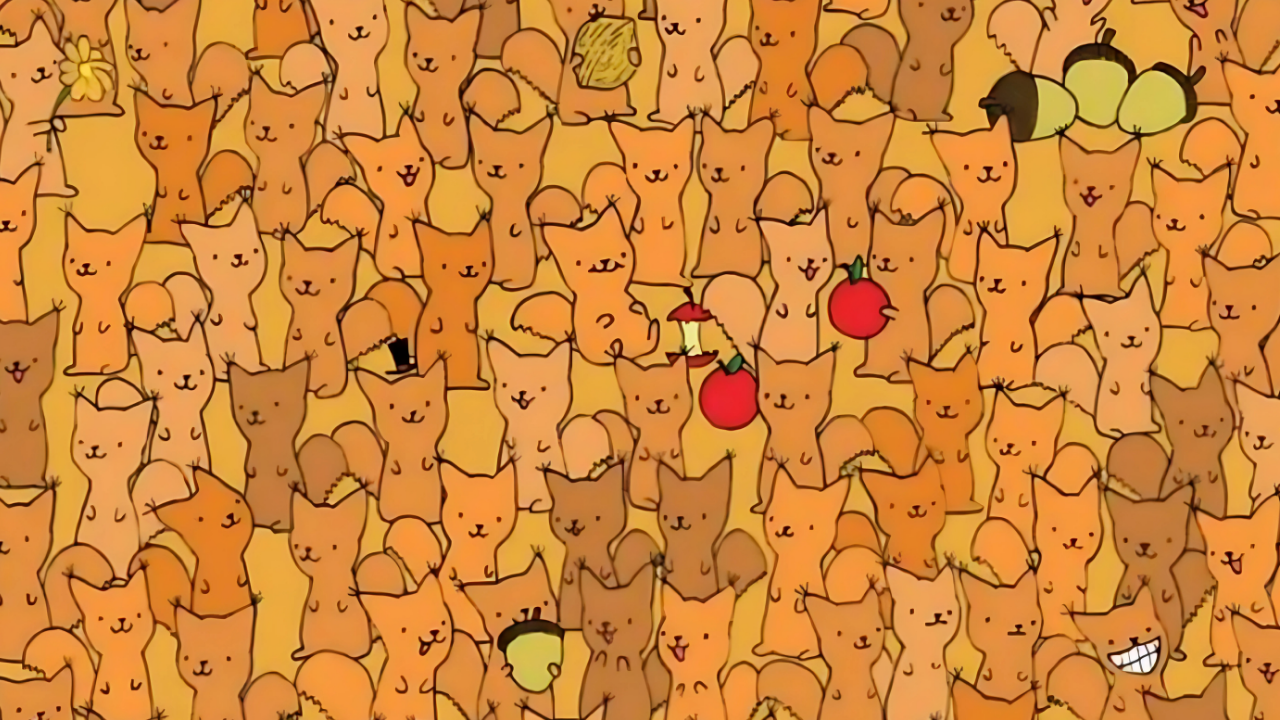
Have you ever stared at something so long your eyes started playing tricks on you? That strange feeling when what you’re looking at isn’t quite what it seems happens to the best of us. Optical illusions have fascinated humans for centuries, challenging our brains and testing the limits of our perception.
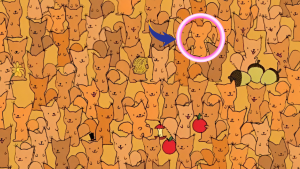
Today, I’m bringing you a particularly tricky visual puzzle that’s been stumping even the sharpest-eyed viewers online. This deceptive image contains a sneaky little mouse hiding in plain sight, and remarkably few people can spot it within the 7-second challenge time.
Why Our Brains Love (and Hate) Optical Illusions
Our visual system didn’t evolve to solve puzzles on smartphone screens. It developed to keep our ancestors alive in environments where spotting predators or finding food quickly meant survival.
When we encounter optical illusions, we’re essentially experiencing the limitations of our perception system. Our brains make quick assumptions based on limited information, and sometimes those shortcuts lead us astray.
The brain processes what our eyes see based on expectations and past experiences. This is precisely why what seems obvious to one person might remain completely invisible to another.
The Science Behind the Challenge
Research shows that regular practice with visual puzzles can actually improve cognitive function. These aren’t just fun diversions—they’re giving your brain a proper workout.
Each time you strain to find that hidden element, you’re strengthening neural pathways. Your brain is literally building better connections while you search for that elusive mouse!
Stanford neuroscientists discovered that people who regularly engage with visual puzzles show enhanced activity in the visual cortex. The more you challenge your visual perception, the better it tends to perform over time.
The Hidden Mouse Challenge Explained
The particular challenge I’m sharing today requires focus and attention to detail. Within the seemingly ordinary image lies a cleverly camouflaged mouse.
Most people initially scan the obvious areas, missing the mouse entirely. The creator designed this illusion specifically to exploit our brain’s tendency to overlook certain patterns.
The time limit of 7 seconds adds pressure that further complicates the task. Under time constraints, our visual processing system sometimes makes hasty judgments that lead us away from the solution.

Tips to Improve Your Visual Detection Skills
Struggling to find hidden elements in puzzles like these? Don’t worry—there are techniques that can help improve your performance on visual challenges.
Try moving your eyes methodically across the image rather than letting them jump around randomly. Many people miss hidden elements because their gaze never lands in the right spot.
Another helpful approach is to squint slightly while looking at the image. This can sometimes reduce distracting details and help the hidden element stand out more clearly.
Taking quick breaks to rest your eyes can also help. Visual fatigue makes these puzzles significantly more difficult, so give your eyes a moment to reset if you’re struggling.
What Your Performance Reveals About Your Visual Perception
Did you find the mouse within 7 seconds? If so, congratulations! You have above-average visual processing abilities and excellent attention to detail.
Those who take longer shouldn’t feel discouraged. Different brains process visual information in different ways, and these puzzles aren’t perfect measures of intelligence or perception.
Some research suggests that creative thinkers often struggle more with these specific types of challenges. Their brains naturally look for multiple possibilities rather than focusing on finding one “correct” answer.
The Connection Between Visual Puzzles and Brain Health
Neurologists consistently recommend visual puzzles as part of maintaining cognitive health. These challenges stimulate multiple brain regions simultaneously, creating a comprehensive mental workout.
The combination of focus, pattern recognition, and visual processing engages different neural networks. This broad activation is similar to what happens during physical cross-training for athletes.
Regular engagement with visual challenges may even help maintain cognitive function as we age. Several studies suggest these activities could help slow age-related decline in visual processing speed.
Beyond Entertainment: Practical Applications of Visual Perception
These seemingly simple puzzles have real-world significance beyond mere entertainment. Many professions rely heavily on advanced visual perception skills.
Medical professionals, particularly radiologists, use similar visual detection abilities to identify subtle abnormalities in scans. Their trained eyes can spot crucial details that untrained observers would miss completely.
Wildlife biologists tracking camouflaged animals in their natural habitats rely on the same perceptual abilities. The difference between spotting or missing a well-hidden creature can significantly impact research outcomes.
Even in everyday life, sharp visual perception helps with tasks from driving safely to finding lost items. The skills you develop through these puzzles translate to practical advantages.
How Children Benefit From Visual Puzzles
Children often excel at these challenges, sometimes outperforming adults. Their developing visual systems haven’t yet established all the shortcuts and assumptions that can hinder adult perception.
Including visual puzzles in children’s activities supports crucial developmental milestones. These exercises strengthen visual discrimination skills that later help with reading and mathematics.
Parents and educators increasingly incorporate these types of challenges into learning materials. They recognize the cognitive benefits extend far beyond the momentary fun of solving the puzzle.
The Surprising History of Optical Illusions
Humans have been creating and solving optical illusions for thousands of years. Ancient Greek architects deliberately incorporated visual tricks into buildings to create specific perceptual effects.
Medieval artists embedded hidden images in their works, often as symbolic messages for those perceptive enough to find them. These historical examples show our long-standing fascination with visual trickery.
The modern study of optical illusions began in earnest during the 19th century. Scientists realized these visual curiosities could reveal fundamental truths about how our brains process information.
Today’s digital illusions build on this rich history while utilizing modern understanding of cognitive science. What seems like a simple hidden mouse puzzle actually connects to centuries of human inquiry.
Ready for the Solution?
If you’re still searching for that elusive mouse, don’t worry—you’re not alone. Many people need more than the initial 7 seconds to spot our well-hidden rodent friend.
Before revealing the answer, try once more with fresh eyes. Look at the areas you might have overlooked during your first attempt.
Sometimes the solution lies not in looking harder, but in looking differently. Our visual system can get stuck in patterns that prevent us from seeing alternatives.
Have you found it yet? If not, here’s a hint: the mouse isn’t where most people initially look. The creator cleverly used our expectations against us in designing this particular challenge.
FAQs About Optical Illusions and Visual Perception
What causes optical illusions? Optical illusions result from how our brains interpret visual information, making assumptions based on past experiences and expectations that sometimes lead to misperceptions.
Are some people naturally better at solving visual puzzles? Yes, visual processing abilities vary naturally between individuals, with some people having inherently stronger pattern recognition or spatial reasoning skills.
Can I improve my ability to solve optical illusions? Absolutely! Regular practice with various types of visual puzzles can strengthen the neural pathways involved in visual processing and improve performance over time.
Do optical illusions work the same way for everyone? No, cultural background, age, expertise, and individual neurological differences can all influence how people perceive and solve optical illusions.
Why do I sometimes see something different than what others see in the same image? Your unique brain processes visual information based on your specific experiences and expectations, which can lead to different interpretations of ambiguous images.
Are optical illusions just for fun, or do they have scientific value? While entertaining, optical illusions provide valuable insights into human visual processing and have contributed significantly to our understanding of perception and cognition.
Why do we enjoy being “tricked” by optical illusions? The challenge of resolving visual contradictions activates reward centers in our brains, making the eventual “aha!” moment particularly satisfying.
Can animals perceive optical illusions? Many studies show that various animals, including primates and birds, respond to certain types of optical illusions, suggesting some shared perceptual mechanisms across species.
Do optical illusions work for people with visual impairments? Some types of illusions may work differently or not at all for people with specific visual impairments, depending on which aspects of visual processing are affected.
What’s the difference between an optical illusion and a brain teaser? Optical illusions specifically exploit quirks in our visual perception system, while brain teasers can involve various cognitive processes including logic, language, and problem-solving.
Whether you found the mouse in record time or are still searching, I hope this challenge brought a moment of focus and fun to your day. Visual puzzles remind us that what we see isn’t always what’s really there—a humbling reminder of the fascinating complexities of human perception.
